Incidence and mortality of gynecological cancers
Despite the many recent advances in cancer diagnosis and treatment, gynecological
cancers are responsible for approximately 25.000 deaths per year and are the third
leading cause of cancer-related mortality in women in the United States 1. Most of
the deaths are caused by tumors that metastasize prior to the onset of symptoms,
in part because there are no accurate screening methods for these cancers and they
are often diagnosed at a late stage.
 Worldwide, more than 200.000 deaths per year
from gynecological cancers are expected 2,3.
Worldwide, more than 200.000 deaths per year
from gynecological cancers are expected 2,3. 
The high mortality associated with undetected gynecologic malignancies has made
the development of an effective screening tool a high priority.
More then 22.000 women with a positive diagnosis in the U.S.1
More then 14.000 deaths each year 1

Ovarian cancer is less common but more lethal. It is often diagnosed at a late stage, when the 5-year survival rate is less than 30%.
More then 62.000 new cases
diagnosed in the U.S. each year 1
More then 11.000 women die each
year from the disease 1
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy.
1) Howlader et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014 (National Cancer Institute, 2017).
2) Bray et al.. Int. J. Cancer 10.1002/ijc.27711 (2012).
3) International Agency for Research on Cancer, GLOBOCAN 2008 v1.2, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase
No. 10; http://globocan.iarc.fr.

A Pap-Based DNA Test for Early Detection of Endometrial and Ovarian Cancers
Cervical fluid samples gathered during routine
Pap tests are the basis of a revolutionary
screening test for gynecological cancers
Prevention and early detection remain essential to decreasing cancer mortality.
For many years, researchers have strived to develop a feasible and reliable way to
detect early-stage gynecological cancers.
The introduction of routine screening for cervical cancer with cytology (the
Papanicolaou test, otherwise known as “Pap smear”) has dramatically decreased the
incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in the screened population, by permitting
the detection of early-stage, surgically curable cervical tumors and their precursors


Unfortunately, the identification of
malignant cells from endometrial
and ovarian carcinomas in cervical
cytology specimens is relatively
uncommon. Microscopic examination
cannot always distinguish them from
cervical carcinomas, or from more
benign conditions.

Screening DNA in Pap smears
has the potential to increase the
rate of early-stage detection of
endometrial and ovarian cancers
in women who do not have any
symptoms. This DNA could be
exploited to detect somatic
mutations in tumor DNA released
from endometrial and ovarian
cancers shed cells accumulating
in the cervix.
How the test works
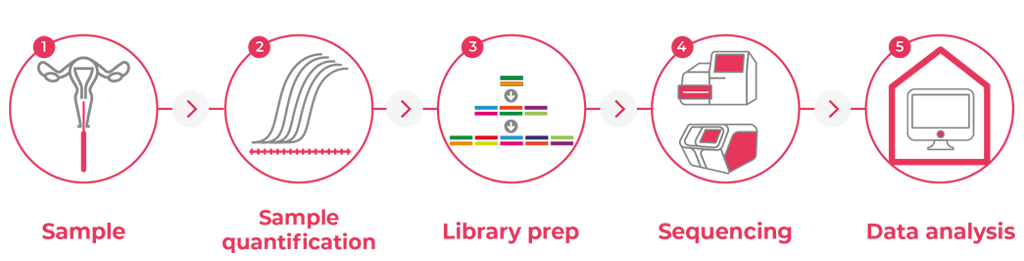
A Groundbreaking technology allowing for a genetic analysis that is revolutionary
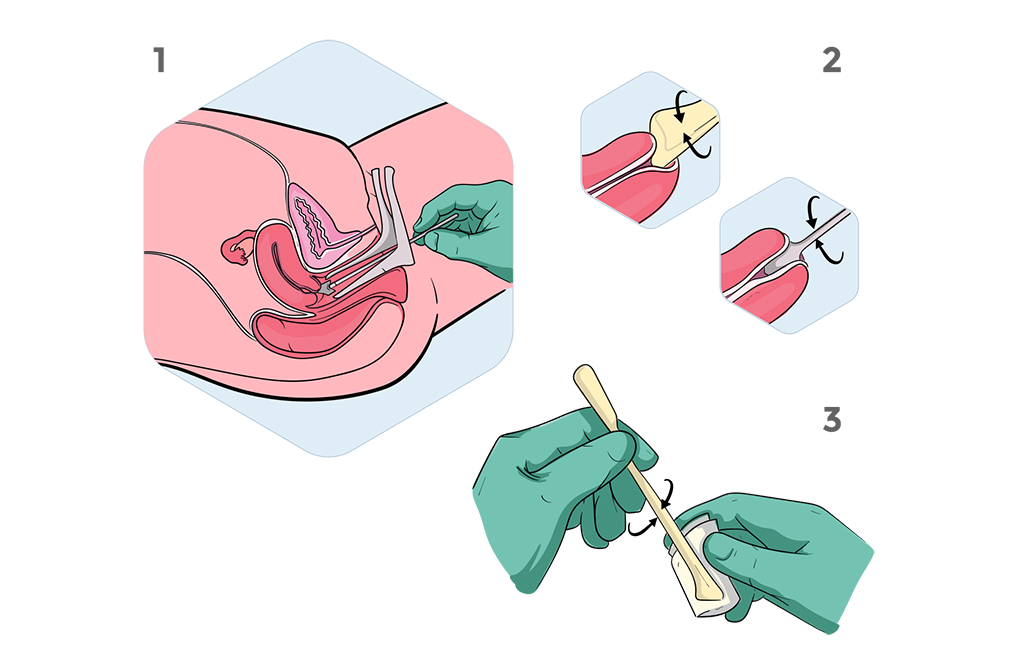
Sampling Procedure
Simple and fast procedure
Cancer cells are sampled during routine Pap tests
with a brush (a “Pap brush”) that is inserted into
the endocervical canal to scrape the surface of the
cervix and then rinsed in a liquid-filled vial containing
preservative fluid.
For the detection of cervical cancers, cells from the
fluid are applied to a slide for cytologic examination
(the classic Pap smear). From the remaining sample,
somatic mutations could be detected in tumor DNA of
women with ovarian or endometrial, ovarian and
cervical cancers.
Indications
PAPNext™ test is meant for preventative surveillance of highrisk
populations.
It may be beneficial for (but not limited to):
 Genetic predisposition
Genetic predisposition
Patients with inherited predisposition to ovarian cancer, such as those with germline mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene or those with Lynch syndrome, caused by a germline mutation in MSH2 or MLH1 genes.
 Risk factors
Risk factors
Patients who are at high risk for gynecologic cancers, e.g. because of hereditary factors, obesity, or symptoms such as postmenopausal or dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
 Positive screen
Positive screen
Patients with positive conventional cytology screening test results.
 Family History
Family History
Patients with a significant family history of endometrial and ovarian cancer.
 Early detection
Early detection
Any patient wishing to undergo to preventative surveillance for endometrial, ovarian and cervical cancers.
Benefits
A new dimension of screening for
gynecologic cancers
Early detection of endometrial and ovarian cancers based on genetic analyses of
DNA recovered from the fluids obtained during a routine Papanicolaou (Pap) test
PAPNext™ is a screening test that identifies cancer-related alterations
in DNA obtained from cervical fluids gathered during a routine Pap test
PAPNext™
test can detect endometrial and ovarian cancers at their
early stage.
Earlier detection of cancer could lead to earlier treatment and potentially
better outcomes for patients.
PAPNext™
test leverages the existing cervical screening strategy with an
advanced sequencing technology to assess for DNA mutations in 30 genes
that are commonly mutated in endometrial, ovarian and cervical cancers,
providing a cost-effective screening approach for these gynaecologic
malignancies.

Science behind the test
A recent study4 demonstrated the ability to detect endometrial and ovarian cancer
based on genetic analysis of DNA recovered from cervical fluids obtained during a
routine Papanicolaou (Pap) test. When an advanced sequencing technology was used to screen Pap test samples,
gathered from women endometrial and ovarian cancer, for somatic mutations in
DNA, the assay identified cancer-related alterations.

In addition, no cancer-related alterations were detected in samples collected from bwomen without cancer.
4) Kinde et alSci Transl Med. 2013 Jan 9;5(167):167ra45)
5) Wang et al. Sci Transl Med. 2018 Mar 21;10(433). pii: eaap8793.
Methodology
In-depth analysis of genes with advanced technology
PAPNext™
test is performed using highly advances Next Generation Sequencing
(NGS) technology to screen for tumor DNA mutation in 30 genes that are commonly
mutated in endometrial and ovarian cancers.
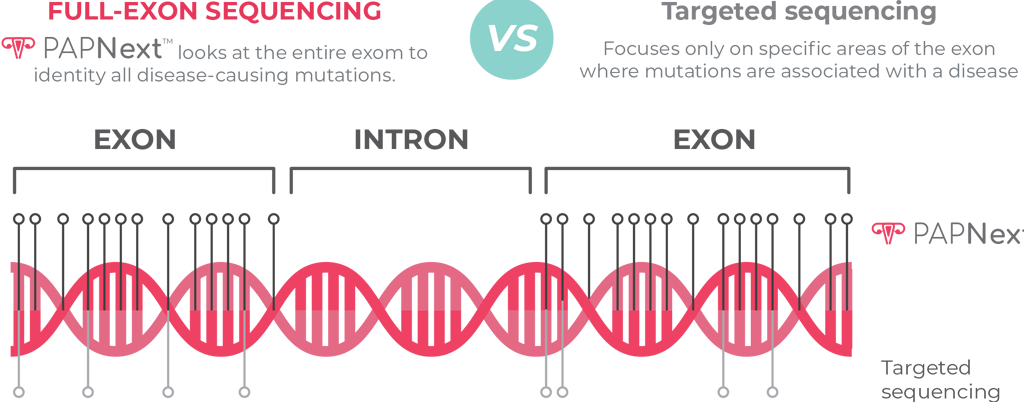
The technology is based on full exon sequences, at high sequence dept, of all genes
included in the panel, which allow a more comprehensive analysis of each gene
investigated.
 Advanced bioinformatic
analysis for variant
interpretation to deliver the
greater accuracy.
Advanced bioinformatic
analysis for variant
interpretation to deliver the
greater accuracy. 
Analysis of NGS data is a complex process,
imposing challenging requirements both in terms
of computing resources and software.
PAPNext™ test uses powerful custom-built bioinformatics
solutions to support variant analysis that enables
fast, reliable and highly accurate results.
When a variant is detected during the sequencing
process, its pathogenicity will be investigated using
a sophisticated software. A team of board-certified
geneticists provide expert interpretation and clearly
explained reports.

advanced molecular diagnostics solutions in reproductive genetics using state-of-the art technologies

Test performed in Italy
(Rome or Milan)

Fast TAT:
15 working days

20 years
experience

Personalized genetic counseling

Laboratories ISO 17025 accredited

Test available
worldwide

Over 200.000
genetic tests/year.

Dedicated R&D team
Results
Understanding PAPNext™ results
POSITIVE RESULT
This result shows that the test identified clinically relevant somatic
mutation(s) in tumor DNA, in one or more of the targeted genes
screened. A patient with a positive test result should be referred for genetic
counselling before any medical decisions are made.
 Genetic counselling
Genetic counselling
Genetic counselling is essential for any patient. Genoma
will provide a genetic counselling session for those patients
that screen positive, and the service is included in the cost
of the test.
It aids the patients in medical comprehension and enhances
patient satisfaction by providing access to experts who are
skilled at explaining genetics risk in terms patients can
understand.
NEGATIVE RESULT
This result shows the test has not detected any clinical relevant
mutation in the targeted genes screened.
A single test cannot always detect all possible genetic changes that
cause a particolar cancer condition, hence a negative results do not
completely rule out the presence of malignancies screened.
 PAPNext™ Technical Report
PAPNext™ Technical Report
 5 easy STEPS
5 easy STEPS

Order PAPNext shipping kit

Fill in all requires TRF information

Collect the sample using the Pap brush

Ship the sample to Genoma Lab

Receive results in 15 working days
CONTACT US
Information request for PAPNext™ test
Contact us by calling the Contact Center +39 06164161500 (12 lines PBX) to discover how you can perform PAPNext™ test or fill out the form below. Your personal information will be used exclusively to satisfy your request, in the absolute respect of your privacy.